The Complete Guide to AI Contract Review in 2026
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How AI Reads Legal Language: The NLP Foundation
- Machine Learning Approaches: Teaching AI to Think Like a Lawyer
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Grounding AI in Real Contracts
- Accuracy Benchmarks: Actual System Capabilities
- Time Savings and Efficiency: Data Insights
- Playbook Enforcement and Automated Redlining
- Setup Considerations for Legal Teams
- Manual Review vs. AI Review: A Real Comparison
- The Hallucination Problem: Why Legal AI Must Be Purpose-Built
- Future Directions and Emerging Capabilities
- Bottom Line
- Introduction
- How AI Reads Legal Language: The NLP Foundation
- Machine Learning Approaches: Teaching AI to Think Like a Lawyer
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Grounding AI in Real Contracts
- Accuracy Benchmarks: Actual System Capabilities
- Time Savings and Efficiency: Data Insights
- Playbook Enforcement and Automated Redlining
- Setup Considerations for Legal Teams
- Manual Review vs. AI Review: A Real Comparison
- The Hallucination Problem: Why Legal AI Must Be Purpose-Built
- Future Directions and Emerging Capabilities
- Bottom Line
Introduction
Legal teams manage numerous contracts. A mid-sized law firm reviews thousands annually, each requiring lawyer time for risk assessment, obligation extraction, and compliance. AI contract review is now essential. However, not all AI is equal. A Stanford study found general AI hallucinates legal advice 69% of the time, while purpose-built legal AI tools achieve over 90% accuracy, with some models preferred by lawyers 97% of the time over manual review. This guide explains AI contract analysis, system capabilities, and how legal professionals should evaluate and implement them in 2026.
How AI Reads Legal Language: The NLP Foundation
Feeding a contract into an AI system doesn’t involve a robot lawyer reading the text. It uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to break text into components. Understanding these mechanics helps identify overselling of capabilities.
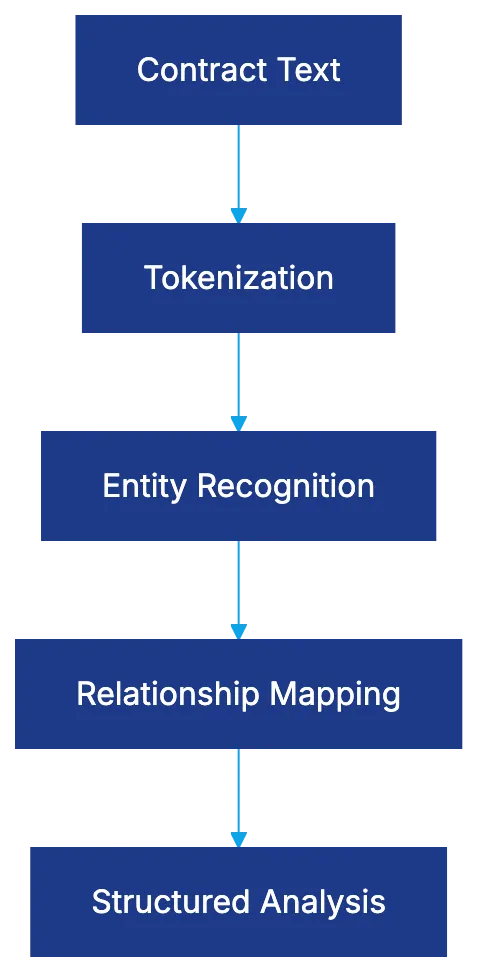
NLP begins by breaking contracts into structural elements. AI identifies sentence boundaries, tokenizing text, then applies part-of-speech tagging. The key phase is entity recognition, identifying parties, terms, dates, and monetary amounts. This foundational layer informs the analysis.
NLP Processing Pipeline:

Relationship mapping follows. AI links entities to obligations and understands how clauses modify each other using dependency parsing. It recognizes negations and modal verbs like “shall,” “may,” “must,” and “should,” which vary in legal significance.
Machine Learning Approaches: Teaching AI to Think Like a Lawyer
NLP lets AI read contracts; machine learning lets it understand them. Different ML methods have various strengths and limitations.
Supervised learning is crucial for contract AI. Lawyers label thousands of examples to train the system on patterns in indemnification clauses or liability provisions. The quality depends on the data, and datasets like CUAD standardized benchmarks.
Machine Learning Training Approach:

Unsupervised learning lets AI find patterns but may not grasp legal significance. Transformer models, like BERT and DeBERTa, improve context understanding by considering surrounding words, enhancing AI contract analysis.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Grounding AI in Real Contracts
RAG System Architecture:
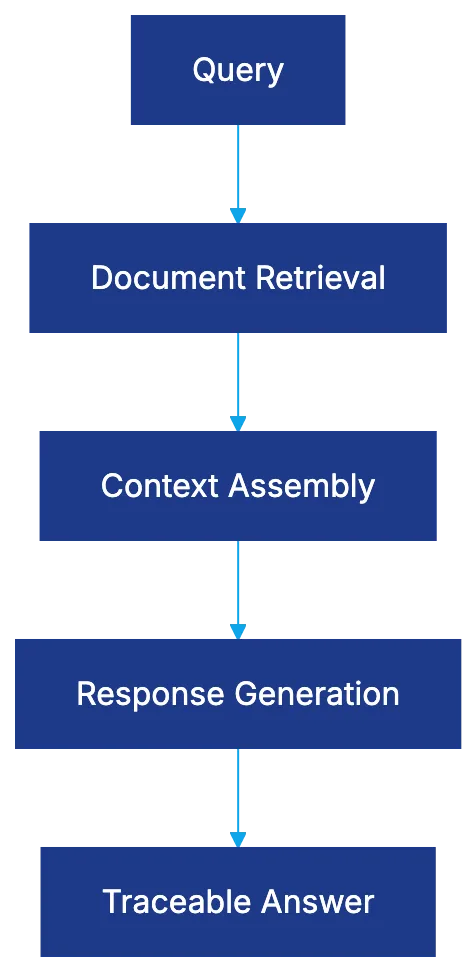
RAG combines language understanding with document retrieval to tackle general AI’s hallucination issue. While traditional AI classifies and extracts, RAG systems can retrieve relevant sections and generate responses from actual contract language, offering traceability and handling contract-specific defined terms more effectively.
Accuracy Benchmarks: Actual System Capabilities
Kira Systems boasts over 90% accuracy for standard clause identification. LegalOn scored 92 out of 100 on playbook adherence, and Harvey’s benchmark found 97% of lawyers preferred AI analysis over manual review. Gartner also highlights AI and contract analytics as urgent priorities for general counsel. Accuracy can decline with unusual clauses or industry-specific provisions, showing the need for context-specific tech choices.
Time Savings and Efficiency: Data Insights
Legal departments report 70% to 85% time savings on initial analysis using AI. It handles extraction and initial categorization, allowing lawyers to focus on deeper analysis. For example, a firm increased throughput from 12 to 40 contracts per week per attorney. Forbes notes that AI can reduce review time by 99.97%, leading to significant cost savings.
Playbook Enforcement and Automated Redlining
AI automates playbook enforcement, comparing contracts against standards and flagging deviations. Redlining suggests changes to align contracts with the playbook and generates explanatory memos for business teams.
Setup Considerations for Legal Teams
AI Implementation Process:
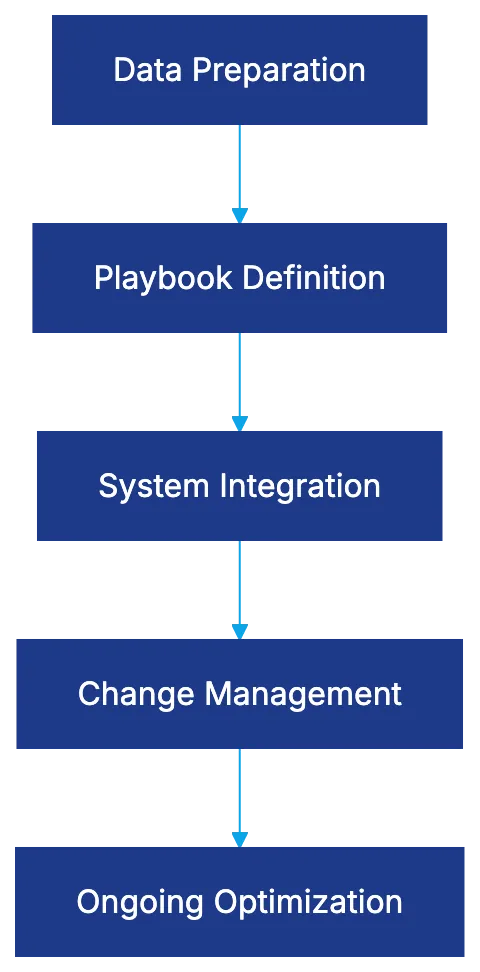
Successful AI implementation requires data preparation, defining playbooks, system integration, and change management. Key considerations include vendor training data, model update frequency, and meeting data security requirements.
Manual Review vs. AI Review: A Real Comparison
AI performs extraction and categorization in minutes, enabling lawyers to focus on evaluation and judgment, improving consistency and managing complexity, especially with novel contract structures or historical language.
The Hallucination Problem: Why Legal AI Must Be Purpose-Built
General AI models hallucinate legal advice due to a lack of grounding in legal sources. Stanford’s findings highlight the importance of purpose-built legal AI, trained specifically on legal text, like the CUAD dataset.
Future Directions and Emerging Capabilities
AI contract review is evolving quickly, with advancements in multi-modal analysis, negotiation assistance, predictive analytics, real-time collaboration, industry-specific models, and cautious autonomous contract drafting.
Bottom Line
AI contract review is now a practical and effective tool. Purpose-built legal AI systems achieve over 90% accuracy, delivering time savings and consistency. Understanding the capabilities and limitations ensures successful implementation, starting with standardized contract types and expanding as trust and competence build. This approach enables legal teams to provide strategic advice relying on actual legal expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I determine if a legal AI tool is suitable for my firm?
To evaluate a legal AI tool, consider its accuracy benchmarks, data security measures, and ease of integration with your existing systems. Look for systems with proven results, particularly those that have been validated through independent studies, such as accuracy rates above 90%. Additionally, ensure that the tool is specifically designed for legal applications, as general AI may have a higher chance of error.
What types of contracts can AI effectively analyze?
AI systems excel at analyzing standardized contracts, such as NDAs, service agreements, and employment contracts. However, they may struggle with highly customized agreements or those containing unusual clauses. For optimal results, it's advisable to start with common contract types before gradually progressing to more complex documents.
What should be included in a playbook for AI contract review?
A playbook should outline the standards for acceptable contract clauses, compliance requirements, and specific terms that must be flagged. It serves as a guideline for the AI, helping it understand which aspects of a contract are critical and how to handle deviations. Regular updates to the playbook ensure alignment with evolving legal practices and organizational needs.
What are the expected time savings when implementing AI for contract review?
Legal departments have reported time savings ranging from 70% to 85% in initial contract analysis when using AI tools. By automating data extraction and categorization, lawyers can dedicate more time to critical evaluation and decision-making. This significant reduction in manual workload can enhance overall productivity and throughput.
What is 'hallucination' in the context of AI legal advice?
'Hallucination' refers to instances when AI generates incorrect or fabricated legal advice due to inherent limitations in general AI models. A study indicated that such models can misinterpret legal language, leading to misleading conclusions. This emphasizes the need for legal AI systems that are purpose-built and trained on relevant legal texts to enhance reliability.
How do I handle the data security concerns when using AI tools?
When implementing AI tools, ensure that the provider complies with relevant data protection regulations and employs robust encryption methods for data handling. Evaluate the vendor's security protocols and assess how they manage sensitive legal information. Regular audits and customized security practices can further protect your firm's data from potential breaches.
What are the latest advancements in AI contract review technology?
Recent advancements include multi-modal analysis, which integrates text, images, and other formats, as well as enhanced predictive analytics for estimating contract outcomes. AI tools are also evolving to assist with real-time negotiation and collaboration, offering more contextual understanding of terms. Industry-specific models are emerging to cater to niche requirements, improving overall contract management efficiency.
Related Articles

What Makes Juro Stand Out in CLM Solutions
Discover how Juro revolutionizes contract management for mid-market teams with its AI-native and in-browser approach.
Streamline In-House Legal Teams with Wordsmith Legal
Discover how Wordsmith Legal helps in-house teams automate contract management and focus on complex legal matters.
Revolutionizing AI Contract Review with Dioptra AI
Discover how Dioptra AI streamlines contract review with 95% accuracy, enhancing efficiency for in-house legal teams.